Infrastructure architecture¶
This guide provides a general overview of the InvenioILS infrastructure architecture. It is not meant to be a comprehensive guide for each subsystem.
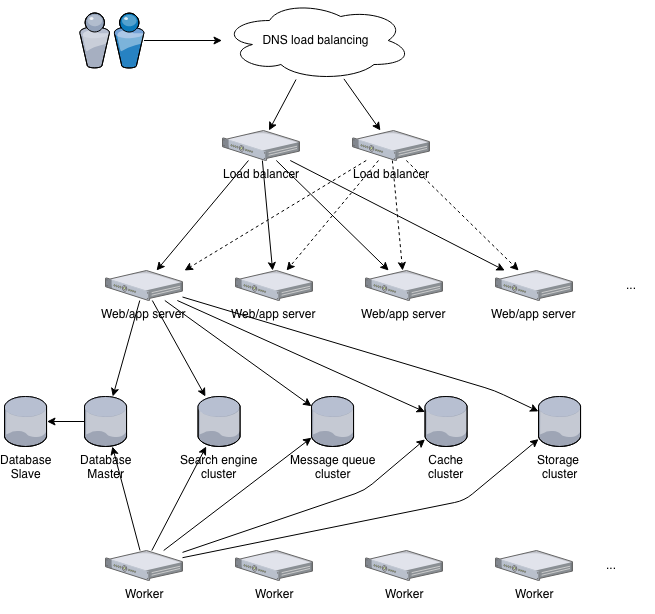
Over all, the InvenioILS infrastructure is a pretty standard web application infrastructure. It consists of:
- Load balancers: HAProxy, Nginx or others.
- Web servers: Nginx, Apache or others.
- Application servers: UWSGI, Gunicorn or mod_wsgi.
- Distributed task queue: Celery
- Database: PostgreSQL, MySQL or SQLite.
- Search engine: OpenSearch (v1 and v2).
- Message queue: RabbitMQ, Redis or Amazon SQS.
- Cache system: Redis or Memcache.
- Storage system: Local, S3, XRootD, WebDAV and more.
Request handling¶
A client making a request to Invenio will usually first hit a load balancer. For high availability you can have more load balancers and balance traffic between them with e.g. DNS load balancing.
Load balancer¶
Request types
The load balancer usually (if it supports SSL termination) allows you to split traffic into three categories of requests:
- static files requests: e.g. JavaScript assets
- application requests: e.g. search queries
- files requests: e.g. downloading files
This way you can dimension the number of connection slots between different types of requests according to available resources. For instance a static file request can usually be served extremely efficiently, while an application request usually takes longer and requires more memory.
Similar, downloading a very large file depends on the client's available bandwidth and can thus take up a connection slot for a significant amount time. If your storage system supports it, Invenio allows you to completely offload the serving of large files to your storage system (e.g. S3).
All in all, the primary job of the load balancer is to manage traffic to your servers according to available resources. For instance during traffic floods the load balancer takes care of queue requests to the web servers.
Backup pages
A load balancer can also direct traffic to a static backup site in case your main web server is down. This is useful in order to communicate with users during major incidents.
Web servers¶
The load balancer proxies traffic to one of several web servers. The web server's primary job is to manage the connections to your application server. A web server like Apache and Nginx is usually much better than an application server to manage connections. Also, you can use the web server to configure limits on specific parts of your application so that for instance you can upload a 1TB file on the Files REST API, but not on the search REST API.
Application servers¶
The web server proxies traffic usually (but not necessarily) to a single application server running on the same machine. The application server is responsible for handling the application requests. Invenio is a Python application, and thus make use of the WSGI standard. There exists several application servers capable of running WSGI python application, e.g. Gunicorn, uWSGI and mod_wsgi.
Storing records¶
Invenio store records as JSON documents in an SQL database. Most modern SQL databases today have a JSON type, that can efficiently store JSON documents in a binary format.
Transactional databases
The primary reason for using an SQL database is that they provide transactions which are very important as data consistency is of utmost importance. Also, database servers can handle very large amounts of data as long as they are scaled and configured properly. Last but not least, they are usually highly reliable as compared to some NoSQL solutions.
Primary key lookups
Most access from Invenio to the database is via primary key lookups, which are usually very efficient in-database. Search queries and the like are all sent to the search engine cluster which can provide much better performance than a database.
Search and indexing¶
Invenio uses OpenSearch as its underlying search engine since OpenSearch is fully JSON-based, and thus fits well together with storing records internally in the database as JSON documents.
OpenSearch furthermore is highly scalable and provides very powerful search and aggregation capabilities. You can for instance make geospatial queries with OpenSearch.
Direct indexing
Invenio has the option to directly index a record in OpenSearch when handling a request, and thus make the record immediately available for searches.
Bulk indexing
In addition to direct indexing, Invenio can also do bulk indexing which is significantly more efficient when indexing large number of records. The bulk indexing works by the application sending a message to the message queue, and at regular intervals a background job will consume the queue and index the records. Also, several bulk indexing jobs can run concurrently at the same time on multiple worker nodes and thus you can achieve very high indexing rates during bulk indexing.
Background processing¶
Invenio relies on an application called Celery for distributed background processing. In order for an application server to reply faster to a request, it can offload some task to asynchronous jobs. It works by the application sending a message to the message queue (e.g. RabbitMQ), which several Celery worker nodes continuously consume tasks from.
For example a background task can be sending an email or registering a DOI.
Multiple queues
The background processing supports multiple queues and advanced workflows. You could for instance have a low priority queue that constantly runs X number of file integrity checks per day, and another normal queue for other tasks like DOI registration.
Cronjobs and retries
Celery also supports running jobs at scheduled intervals as well as retrying tasks in case they fail (e.g. if a remote service is temporarily down).